Patau Syndrome
The frequency of Patau Syndrome increases with an increase in maternal age. Generally as women pass the age of 35 years old, the risk of having a baby with Trisomy 13 increases. It is reported that Trisomy 13 occurs in 1/5000 to 1/12,000 live births. The estimated annual number of cases in the United States in 2004-2006 has reported to have been 528.
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
The prevalence of FOP has been estimated at 1 case per 1.64 million persons in the United Kingdom. It is believed to have occurred in virtually 1 in 2 million people worldwide. Fewer than 200 cases have been determined worldwide. FOP usually starts in early infancy. FOP is more common in females than in males.
Have you ever pondered upon how you actually developed your appearance? This can be explained through the existence of our genes, which are inherited from each of the parents thus creating every individual's distinguishing features. Genetics is the broad scientific study of genes and heredity. The foundation of inheritance and in turn the revolution of genetics was discovered by Gregor Mendel, who experimented with pea plans to reach to the ultimate theory of heredity.
Patau Syndrome title
PATAU SYNDROME
Patau Syndrome

Natalia-Marie. Diagnosed with full Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome
Patau Syndrome, also known as Trisomy 13 and Trisomy D, is a autosomal genetic disorder which is caused due to a chromosomal deviation. It happens to occur due to the presence of an additional chromosome 13 in some or all of the body's cells as a result of nondisjunction during the phase of meiosis. Patau Syndrome may also be caused due to translocation when a section of chromosome 13 attaches itself to another chromosome during the creation of sex cells. The most common symptoms of Trisomy 13 include the following: Cleft lip or palate, clenched hands, decreased muscle tone, extra fingers or toes, deafness as well as mental retardation. Sudden seizures are also one of the characteristics of individuals diagnosed with Patau Syndrome. It has been determined that no particular treatment or therapy exists for this genetic order; however physicians do focus on the individual physical problems with each new born baby. Diligent efforts are conducted toward treating heart defects or cleft facial structures. Furthermore genetic assistance and counseling is facilitated in order to provide support to the parents of an offspring with Trisomy 13 or prospective parents. Trisomy 13 patients often undergo severe neurological obstruction along with complicated heart defects thus the possibility of survival are likely to be extremely difficult. The chances of delivering a child with this disorder increase with an increase in a woman's age.
Patau Syndrome

Karyotype of Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome
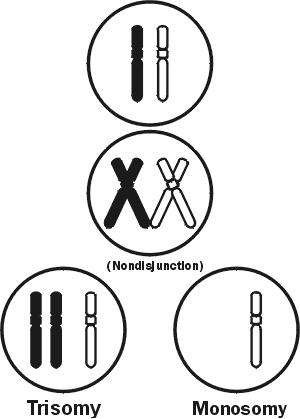
Trisomy 13 is caused due to nondisjunction
FOP title
FIBRODYSPLASIA OSSIFICANS PROGRESSIVA
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva

Malfunctioned bones- FOP
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) is a genetic disorder which involves discrepancies in muscle and connective tissues, causing tendons and ligaments to gradually be replaced by bone. This process of replacement is called ossification. In particular, the specific disorder causes skeletal muscles and soft tissues to transform into bone. Such malfunctions eventually lead to having difficulties in movement and in turn affect joints such as knees, wrists, shoulders, and spine. FOP is caused due to mutations in the activin A receptor, type I (ACVR1) gene. The normal gene originally exists to provide the body with instructions on how to produce the activin receptor type I protein, which is in many body tissues such as skeletal muscles. This protein helps in the regulating the growth and development of muscles and bones. However, a mutation in the ACVR1 gene can cause too much bone to grow which leads to the disorder of FOP.
This particular disorder is passed down as an autosomal dominant trait, which means that one copy of the mutated gene in each cell is sufficient thus there are higher probabilities of developing a child with FOP. Individuals diagnosed with FOP are usually discerned by malformed big toes, excessive bone growth, and limited body movements (joints,knees, wrists, shoulders, spine, and neck). Disappointedly, an effective treatment or therapy has yet not been discovered. Surgery may not be the most desirable alternative as to removing the excess bones because the process often leads to even more bone formation. However, physicians are indeed finding some success in developing a drug that may help control bone growth.
FOP

Mutation occurs in Activin Receptor Type I Protein
FOP genetic pattern

Chances of inheriting the disorder through genetics[autosomal dominant]
Slide Show Title
View the slideshow for more pictures and information on Patau Syndrome!
Patau Syndrome Slide Show
fop slide show title
View the slideshow for more pictures and information on FOP!
FOP slide show
About Me
- Sheliza
- Atlanta, Georgia, United States
- Hello! My name is Sheliza Fayyaz and I am currently a student at Peachtree Ridge High School. This is my senior year so I am extremely excited about the prospects of graduation! I have recently moved to Atlanta, but I am originally from Chicago. Overall, I think Georgia is a very interesting state because it's quite different from where I have usually lived before. However, I certainly do miss Chicago, particularly because of the snow during the winter season! I am a very quiet person by demeanor, but I love to meet new people and make new friends. Two of my passions are writing innovating poems and scripts and playing piano. As far as outlooks for my career is concerned, I want to become and work as a neurologist.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment